Gsoc Final Evaluation
Following are my list of contributions during the GSoC period.
HPXCL Repo Link: https://github.com/STEllAR-GROUP/hpxcl
List of Pull Requests: https://github.com/STEllAR-GROUP/hpxcl/pulls?utf8=%E2%9C%93&q=is%3Apr%20author%3AMADHAVAN001%20
List of Issues: https://github.com/STEllAR-GROUP/hpxcl/issues?utf8=%E2%9C%93&q=is%3Aissue%20author%3AMADHAVAN001%20
Mandelbrot Example in HPXCL CUDA
Pull Request: https://github.com/STEllAR-GROUP/hpxcl/pull/54
Blog Post: https://madhavan001.github.io/Mandelbrot-hpxcl-example/
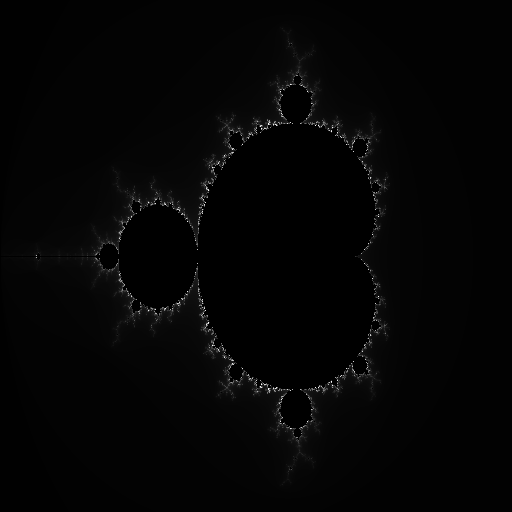
The Mandelbrot example existed previously in HPXCL OPENCL but was missing in HPXCL CUDA. This PR aimed to bring the HPXCL CUDA version examples in parallel with the OPENCL version. The main implementation is to take width, height of the image as input and output the .png of the calculated Mandelbrot set example.
Result Image:

Event Based Code Profiling of Mandelbrot HPXCL CUDA
Branch: https://github.com/STEllAR-GROUP/hpxcl/tree/mandelbrot_events
Comparative Difference: https://github.com/STEllAR-GROUP/hpxcl/compare/mandelbrot_events?expand=1
Blog Post: https://madhavan001.github.io/Performance-Metrics-events/
Work only for analytical purpose. Will not be merged!
This branch of the code was aimed at profiling the performance of the Mandelbrot Set example using event based profiling mechanism used in CUDA. The code is written in Native CUDA and is aimed only for profiling purposes. The branch was decided not to be merged with master as it doesn’t provide core functionality usable for the users. The above piece of code was also used to understand more about the usage of event based mechanism in synchronization of streams and profiling of kernels, allowing us to understand more about the nature of events in comparison with Native OpenCL.
Surveying Benchmarks for code profiling and comparison
Issue: https://github.com/STEllAR-GROUP/hpxcl/issues/44
Blog Post: https://madhavan001.github.io/Benchmarks-accelerator-devices/
This task was aimed at surveying various benchmarks available for profiling HPC systems and testing their usability in effectively profiling HPXCL CUDA, HPXCL OpenCL and their native versions in CUDA and OpenCL. The benchmarks were thoroughly understood and studied for their applicability in testing the various nuances of the application developed.
After the study, the following benchmarks were chosen for implementation:
- Dense Matrix Multiplication problem. (DGEMM)
- Dense Matrix Transpose (Intel PRK)
- Sparse Matrix Vector Product (Intel PRK)
- Stencil (Intel PRK)
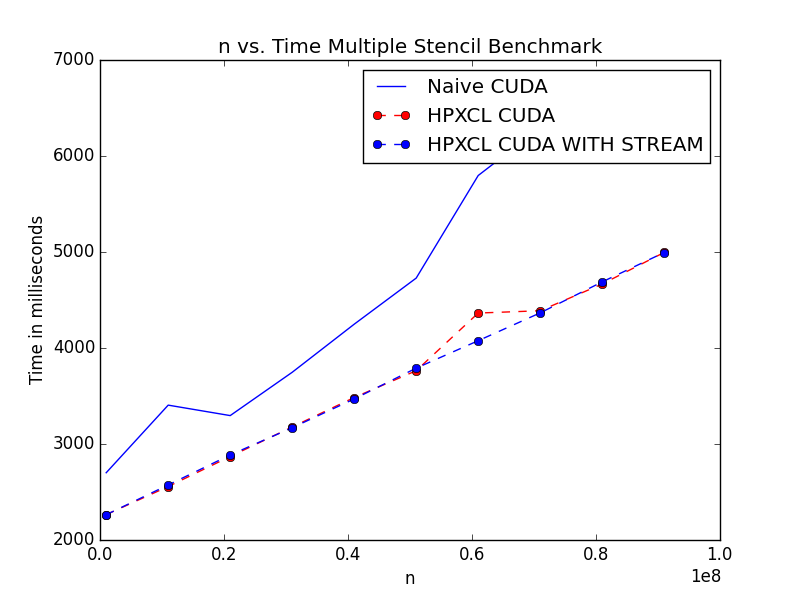
Single Stream Version of HPXCL CUDA
Pull Request: https://github.com/STEllAR-GROUP/hpxcl/pull/57
This PR is aimed at delivering the user an option of queuing the data transfer from host to device/device to host using the default stream (CUDA stream 0). Usually, the data transfer mechanism happens by creating an individual stream for each data transfer which incurs additional overhead in stream management (Creation/Synchronization/Deletion). This gives the user an option to bypass this overhead.
For large data transfers, it is still advisable to use multiple streams.
Plots (Minor performance gains for low values of n: More effective on average or for kernels which require less data transfer):
Stencil Single Stream Comparison
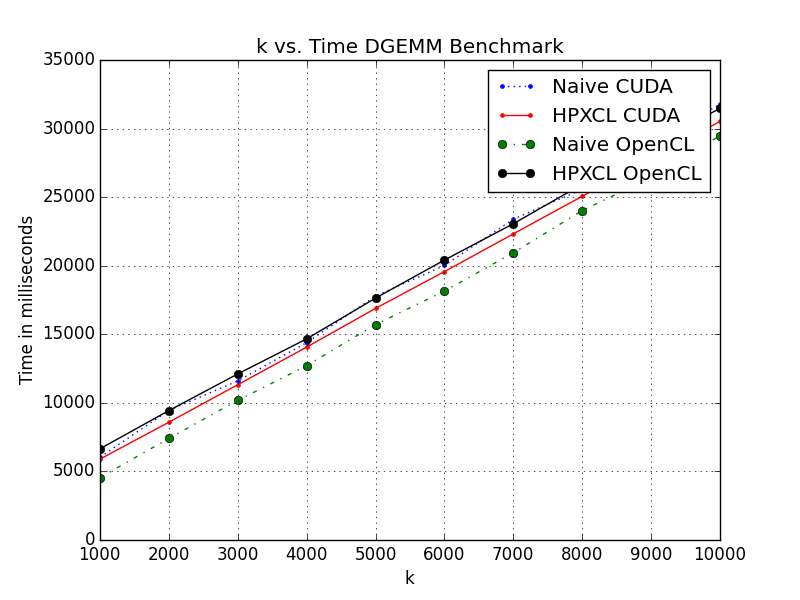
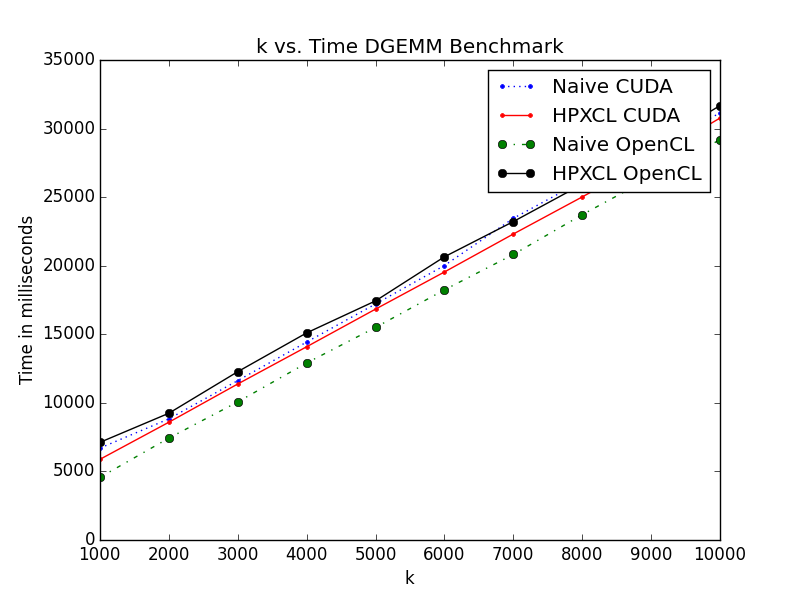
Dense Matrix Multiplication benchmark for HPXCL
Pull Request: https://github.com/STEllAR-GROUP/hpxcl/pull/67
This PR is aimed at implementing the Dense Matrix Multiplication benchmark in HPXCL. Four versions of the algorithm were implemented, namely for the Naïve OpenCL, Naïve CUDA, HPXCL OpenCL and HPXCL CUDA. This is done to understand the bottlenecks of the current system and implement any potential optimizations for the system.
Single Stream Version:
Multiple Stream Version:
Sparse Matrix Vector Product Benchmark
Pull Request: https://github.com/STEllAR-GROUP/hpxcl/pull/69
This PR is aimed at implementing the Sparse Matrix Vector Multiplication benchmark in HPXCL. Four versions of the algorithm were implemented, namely for the Naïve OpenCL, Naïve CUDA, HPXCL OpenCL and HPXCL CUDA. This is done to understand the bottlenecks of the current system and implement any potential optimizations for the system.
Multiple Stream Version:
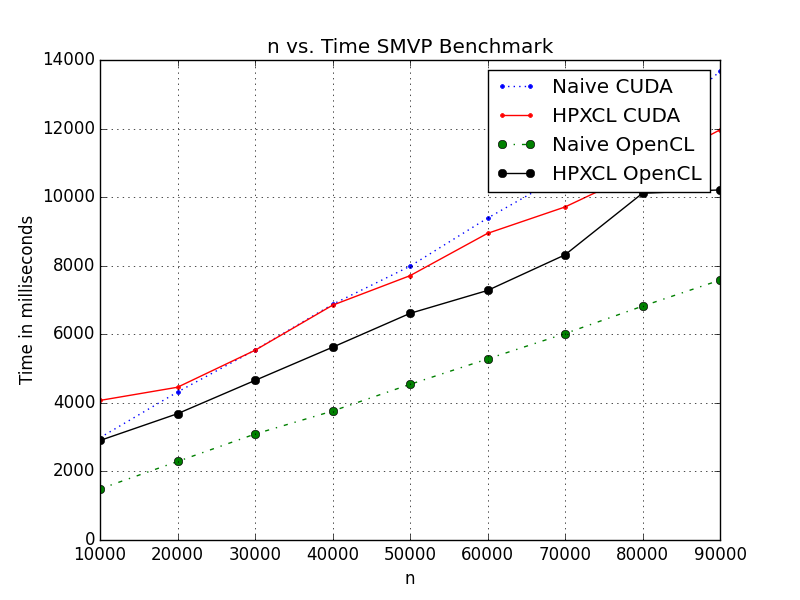
Implementing Benchmarks in OpenCL
Pull Request: https://github.com/STEllAR-GROUP/hpxcl/pull/64 and https://github.com/STEllAR-GROUP/hpxcl/pull/60
Branch has not been merged yet and is work in progress.
The two PRs aimed at adding the OpenCL versions of Stencil, Partition and Stream benchmarks. The benchmarks were not available for the native OpenCL comparison. These PRs aim to help make meaningful comparisons for the future profiling of code. (Some more minor corrections have to be made before PR can be merged with master).
Tests for HPXCL CUDA
Branch: https://github.com/STEllAR-GROUP/hpxcl/tree/cuda_tests
Comparative difference: https://github.com/STEllAR-GROUP/hpxcl/compare/cuda_tests?expand=1
Branch has not been merged yet and is work in progress.
This branch is used for addition of tests for the HPXCL CUDA version. Tests need to be added to check the behaviour of the code in dynamic situations. Unit tests are written to test each individual component function.
Following are the list of Unit tests added:
- Kernel
Each of the following tests is aimed at program compilation and successful kernel execution of ‘Hello World’ program if correct
- Standard test for program compilation and build
- Standard test for program compilation with arguments
- Kernel compilation fail with invalid source name
- Program compilation from Source File
- Invalid Error detection
- Buffer
Each of the following tests are aimed at successful buffer componenent executions.
- Buffer Initialization Test
- Buffer Write with no offset
- Buffer Write with Offset
- Multiple Concurrent Buffer Write
- Buffer Read Test
- Buffer Local Contnuity Test
- Initialization Aimed at testing if the intialization the devices in the test environment holds true.
- Device Test
Tests to check proper device load from localities.
- Load devices from all localities.
- Load only local devices test.
- Load only remote devices test.
- Info Test Test to check if valid device information can be obtained from the environment.
Scripts for generating graphs
Pull Request: https://github.com/STEllAR-GROUP/hpxcl/pull/65
This PR is aimed at providing scripts for running and comparing different algorithms in Rostam. Currently developed for comparing Native CUDA and HPXCL CUDA application, but can be extended to adding HPXCL OpenCL and OpenCL versions of the code and comparing them in plots. Scripts written in python.
Work to be performed after GSoC
Following are the list of tasks to be performed as a continuation to the GSoC work.
- Additional Regression and Performance tests.
- Optimization to HPXCL OpenCL to improve performance to the benchmarks.
- Additional benchmark, namely Dense Matrix Transpose.
All of this work will be summarized and extended as a Research paper, aimed to be submitted to a Conference.