Benchmarks Accelerator Devices
In this post, I shall compare and contrast the different benchmarking tools available for Benchmarking GPU Devices running CUDA and OpenCL. The main aim is to be able to make an informed decision about the benchmarks to be selected for testing HPXCL.
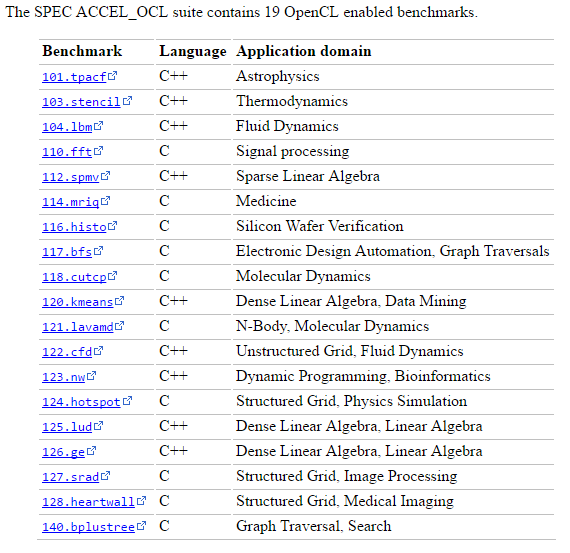
SPEC ACCEL (Standard Performance Evaluation Corporation for Accelerators)
Derived from Parboil Benchmark from the IMPACT Research Group of University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign. [2]
Features:
- Runs under OpenCL and OpenACC APIs.
- Measures performance of accelerator, host CPU, memory transfer between host and accelerator, other drivers and libraries.
- Provide 19 tests for OpenCL enabled benchmarking and 15 for OpenMP enabled benchmarking.
List of Problems:
Lulesh (Livermore Unstructured Lagrangian Explicit Shock Hydrodynamics)
Lulesh Benchmark was co-designed as Lawrence Livermore National Lab.
LULESH is a highly simplified application, hard-coded to only solve a simple Sedov blast problem with analytic answers – but represents the numerical algorithms, data motion, and programming style typical in scientific C or C++ based applications. [1]
Features:
- Both OpenCL and CUDA versions available.
- Contains three main kernels of Hexahedron Volume Calculation, Force Calculation and Calculate linear and quadratic artificial viscosity coefficients.
List of Problems: Sedov Blast Problem
HPCChallenge
This benchmark is used for the testing a number of independent attributes of the performance of High Performance Computer (HPC) Systems. Project sponsored by DARPA High Productivity Computing Systems program, United States Department of Energy and the National Science Foundation [3].
Features:
- Used for benchmarking HPC systems.
- Assumes System under test is a cluster of shared memory multi-processor systems connected to a network.
- Runs with different modes of operation, nodes, for instance single (randomly selected node on a cluster), star (independent copy of results were run concurrently) and global (processors were working in coordination)
List of Problems:
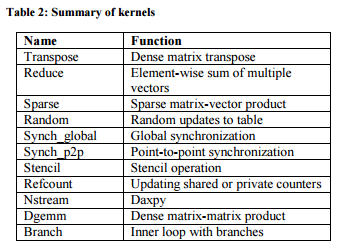
Parallel Research Kernels (PRK)
Developed by Intel Labs. This set of kernels covers the most common patterns of communication, computation and synchronization encountered in parallel HPC applications. [4]
Features:
- Three Kernels are discussed in detail in the paper, namely Refcount Kernel, Sparse Kernel and Branch Kernel.
- Discusses the steps involved in the parallelization of the kernel.
List of Problems:
Details in [4].
NAS Parallel Benchmark
This benchmarks is developed by NASA Advanced Supercomputing division for performance evaluation of Highly Parallel Supercomputers. [7]
Features:
- Five main kernels are available for computation.
- Focused towards measuring the communication bottlenecks of systems under test.
- More suitable for testing MPI-like systems.
List of Problems:
DGEMM
This benchmark is developed by Sandia National Laboratories. The Crossroads/N9 DGEMM benchmark is a simple, multi-threaded, dense-matrix multiply benchmark. The code is designed to measure the sustained, floating-point computational rate of a single node. [6]
Features:
- This benchmark is used for testing individual node in the network.
List of Problems: Dense Matrix Multiplication problem.
NERSC-8(TRINITY BENCHMARKS)
This benchmark is developed by National Energy Research Scientific Computing Center. The set of kernels are used for Trinity System Procurement.[5]
Features:
- There are two kinds of behcmarks: a. Mini Apllications: miniFE, miniGhost, AMG, UMT, GTC, MILC, SNAP, and miniDFT b. Micro Benchmarks: Pynamic, STREAM, OMB, SMB, ZiaTest, IOR, Metabench, PSNAP, FSTest, mpimemu, and UPC_FT
- Detailed problem is explained in the images below.
List of Problems:
References:
[1] Livermore Unstructured Lagrangian Explicit Shock Hydrodynamics (LULESH). Retrieved from: https://codesign.llnl.gov/lulesh.php on: 20 June 2017
[2] The Standard Performance Evaluation Corporation (SPEC). Retrieved from: http://www.spec.org/ on: 20 June 2017
[3] HPC Challenge Benchmark. Retrieved from: http://icl.cs.utk.edu/hpcc/ on: 20 June 2017
[4] The Parallel Research Kernels. Retrieved from: https://pdfs.semanticscholar.org/764f/2039c7e6e1181e33f704d8dc37cb715d9aaf.pdf on: 20 June 2017
[5] NERSC-8(TRINITY Benchmark). Retrieved From: http://www.nersc.gov/users/computational-systems/cori/nersc-8-procurement/trinity-nersc-8-rfp/nersc-8-trinity-benchmarks/ on: 2nd July 2017
[6] DGEMM. Retrieved From: http://www.nersc.gov/research-and-development/apex/apex-benchmarks/dgemm/ on: 2nd July 2017
[7] NAS Parallel Benchmarks. Retrieved From: https://www.nas.nasa.gov/publications/npb.html on: 2nd July 2017